My road to self hosted kubernetes with k3s - argocd
How it works
Argo CD follows the GitOps pattern of using Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state. Kubernetes manifests can be specified in several ways:
- kustomize applications
- helm charts
- ksonnet applications
- jsonnet files
- Plain directory of YAML/json manifests
- Any custom config management tool configured as a config management plugin
Simply put?
argocd connects to github repos where you publish your kubernetes manifests, argocd also connects to your kubernetes clusters. you then define apps in argocd ( which things to run in which cluster ), argocd then ensures stuff matches the state of the github repo, when that updates, argocd rolls out the updates too ).
Installation
I am now going to intall argocd into my local minikube installation
❯ kubectl config use-context minikube
❯ kubectl create namespace argocd
❯ kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
at the point of writing this article we are at argo version 2.0.0
This will create a new namespace, argocd, where Argo CD services and application resources will live.
argocd client
Next i need to be able run argocd commands on my system so i also need to install the cli i ll be grabbing this off AUR
usually id just use
❯ pacaur -S argocd-cli
but they just switched to version 2 which isnt live yet via pacaur so i can grab the last version directly from the community packages:
❯ sudo pacman -U https://archlinux.org/packages/community/x86_64/argocd/download/
alpmtmp.djzaci 14.9 MiB 9.99 MiB/s 00:01 [###########################################] 100%
argocd-2.0.0-1-x86_64.sig 566.0 B 0.00 B/s 00:00 [###########################################] 100%
loading packages...
resolving dependencies...
looking for conflicting packages...
Packages (1) argocd-2.0.0-1
Total Installed Size: 78.28 MiB
:: Proceed with installation? [Y/n] Y
(1/1) checking keys in keyring [###########################################] 100%
(1/1) checking package integrity [###########################################] 100%
(1/1) loading package files [###########################################] 100%
(1/1) checking for file conflicts [###########################################] 100%
(1/1) checking available disk space [###########################################] 100%
:: Processing package changes...
(1/1) installing argocd [###########################################] 100%
:: Running post-transaction hooks...
(1/1) Arming ConditionNeedsUpdate...
access argocd UI
argocd ships with a (very nice) UI. we could expose it as a service/ingress etc but since im running locally a simple port forward will suffice. in order to login we first must grab the admin password
❯ kubectl get pods -n argocd -l app.kubernetes.io/name=argocd-server -o name | cut -d'/' -f 2
❯ kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
the we can login with “admin” and the password returned from the first kubectl command. since we forwarded to port 8080 we ll now login with our cli client via
❯ argocd login localhost:8080
WARNING: server certificate had error: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority. Proceed insecurely (y/n)? y
Username: admin
Password:
'admin' logged in successfully
Context 'localhost:8080' updated
update argocd admin password
after login one should change the admin password
❯ argocd account update-password
link cluster
argocd cli client extracts the cluster information from your ~/.kube/config you can list your clusters with:
❯ kubectl config get-contexts -o name
then we can specify which cluster to add i called my ovh vps cluster “ime”
❯ argocd cluster add ime
prepare github repository
so my prefered way is to generate a new keypair and then add the pubkey of that to github as a deploy key. this limits this keypair read only access - which is ideal for this pipeline.
❯ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f myproject
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in myproject
Your public key has been saved in myproject.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:O07yv+fi78oNN5oC/U1bzWfI4LYSD/SzZhu5qc9fQao loeken@0x00E
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 4096]----+
| |
| |
| . |
| . . o |
| .S. o + = |
| . ..o B.+ *|
| ..+..E=* .o|
| =.o+BX= . |
| o+X#@o. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
❯ ls myproject*
myproject myproject.pub
now head to your github project that contains your code and add the pubkey as a deploy key
link github repository to argocd
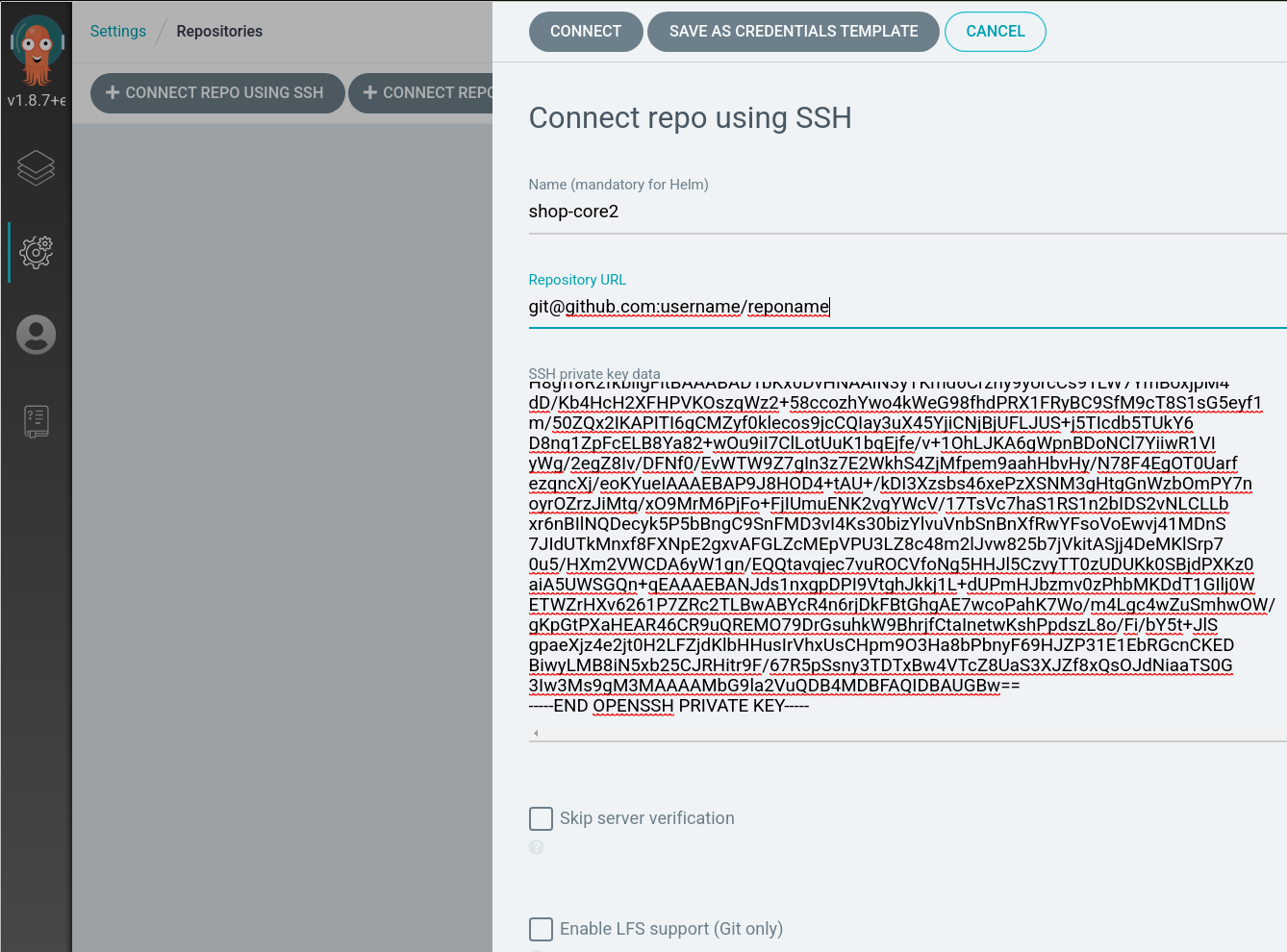
we then use the contents of the privateky ( myproject ) and insert it as the private key in argocd, then it can authenticate with github.
the repository url shouldnt start with https:// but use the git:// syntax ( ssh for auth )
create argocd app
now that we have added a repo ( to read kubernetes yaml manifest from ) and added a cluster to argocd ( where to deploy these manifests too ) - we can now create an app in argocd.
you can either specify manual sync policy - where argocd will only apply configuration changes when you manually tell it to, or selected the automated sync policy, which will check the git repo in certain intervals and automatically apply the configuration changes ( as long as minikube is running ).
when creating a new app we simply select our repository and cluster and click “create”.
backup / restore
this was a bit tricky to me, on my linux my main user has userid 1000 and group 1000 ( normal … ) argocd ships the export tool in their docker image.
https://argoproj.github.io/argo-cd/operator-manual/disaster_recovery/ lets try and follow their documentation.
so since i have this installed in minikube the first thing i saw that could go wrong is that minikube saves certs/keys into ~/.minikube, however the argocd documentation does not mention this, so one would have to either map .minikube as a second volume OR ( what i chose to run )
minikube config set embed-certs true
this will rewrite the ~/.kube/config and base64 encode our keys/certs and inline them into the ~/.kube/config then we can just send this config to the docker container and it includes everything argocd needs to connect to our clusters.
❯ argocd version | grep server
argocd-server: v2.0.0+f5119c0
❯ export VERSION=v2.0.0
❯ docker run -v ~/.kube:/home/argocd/.kube --rm argoproj/argocd:$VERSION argocd-util export
time="2021-04-08T11:24:25Z" level=fatal msg="error loading config file \"/home/argocd/.kube/config\": open /home/argocd/.kube/config: permission denied"
my .kube/config did have the wrong file permissions ( 0600 ) i think argocd expects me to have 0644 so i ll change it to that
❯ sudo chmod 0644 ~/.kube/config
❯ docker run -v ~/.kube/config:/home/argocd/.kube/config --rm argoproj/argocd:$VERSION argocd-util export
time="2021-04-08T11:36:22Z" level=fatal msg="Get \"https://192.168.49.2:8443/api/v1/namespaces/default/configmaps/argocd-cm\": dial tcp 192.168.49.2:8443: i/o timeout"
this also makes sense cause minikube runs it the “minikube” network so let’s add the docker container to that minikube network so it can communicate with argocd running in the minikube network.
❯ docker run --network minikube -v ~/.kube/config:/home/argocd/.kube/config --rm argoproj/argocd:$VERSION argocd-util export
time="2021-04-08T11:36:41Z" level=fatal msg="configmaps \"argocd-cm\" not found"
and this one also explains itself as i ve installed argocd into the argocd namespace - which it does not seem to default to.
❯ docker run --network minikube -v ~/.kube/config:/home/argocd/.kube/config --rm argoproj/argocd:$VERSION argocd-util export -n argocd
at this point you should see output - a yaml markup that includes all our argocd settings. dont forget to add a
> backup.yml
at the end to pipe the output to a file
small backup script
> cd ~/youtbackuplocation
> mkdir backup
> cat backup.sh
#/bin/bash
date=`date '+%Y-%m-%d'`
docker run \
--network minikube \
-it \
-v ~/.kube/config:/home/argocd/.kube/config \
--rm argoproj/argocd:$VERSION \
argocd-util export -n argocd > backup/backup_$date.yaml
> chmod +x backup.sh
> ./backup.shcomments powered by Disqus